AI and Robotics: The Perfect Combination for Warehouse Accuracy
Accuracy is the heartbeat of warehouse operations. A single error in picking, packing, or inventory tracking can ripple through supply chains, leading to delays, returns, and lost customer trust. Traditional manual methods, even with basic automation, often fall short in high-volume environments.
This is where AI and robotics step in. Together, they form a powerful duo that goes beyond mechanical efficiency. Robotics provides the physical execution like lifting, moving, and sorting while AI provides the intelligence to guide decisions. The result? Warehouse accuracy robotics that set new standards for precision, efficiency, and scalability.
In this article, let’s explore how AI robotics warehouse systems are transforming operations, why accuracy matters more than ever, and what future innovations will shape smarter logistics.
The Challenge of Accuracy in High-Speed Logistics
The fundamental challenge in a high-speed warehouse is that human pickers, despite their dexterity, are prone to fatigue and distraction. This leads to common errors like mispicking the wrong product, damaging fragile goods, or miscounting inventory.
Even small error rates are costly when scaled across millions of orders annually. Early warehouse automation solutions addressed speed but struggled with the variability and complexity of inventory:
Fixed Automation (Conveyors, AGVs): Excellent for moving large volumes but lacked the fine motor skills for piece-picking.
Early Industrial Robots: Highly precise for repetitive tasks (like welding) but lacked the perception to handle unstructured environments or a variety of SKU.
The advent of AI changed the game by giving robots the ability to “see” and “think,” turning them from dumb, powerful tools into intelligent, adaptable colleagues. The fusion of AI and robotics ensures that the system not only moves quickly but, more importantly, knows what it is doing with absolute certainty, achieving unprecedented robotic picking accuracy.
Also See: Enhancing Safety and Productivity with Warehouse Robotics
Why Accuracy Matters in Warehousing
In a world where customers expect same-day delivery and error-free fulfillment, accuracy is non-negotiable. With millions of SKUs and complex logistics, manual processes cannot sustain the speed and precision required. This is why warehouse automation solutions are rapidly becoming industry standards.
Consider these impacts:
- Cost of errors: Each mispick or mis-shipment creates return costs, restocking expenses, and wasted labor.
- Customer trust: A single wrong order can reduce brand loyalty. Repeat mistakes can lose a customer permanently.
- Supply chain disruption: Inaccuracies delay not just individual orders but entire workflows across distribution networks.
The Role of Robotics in Warehouse Accuracy
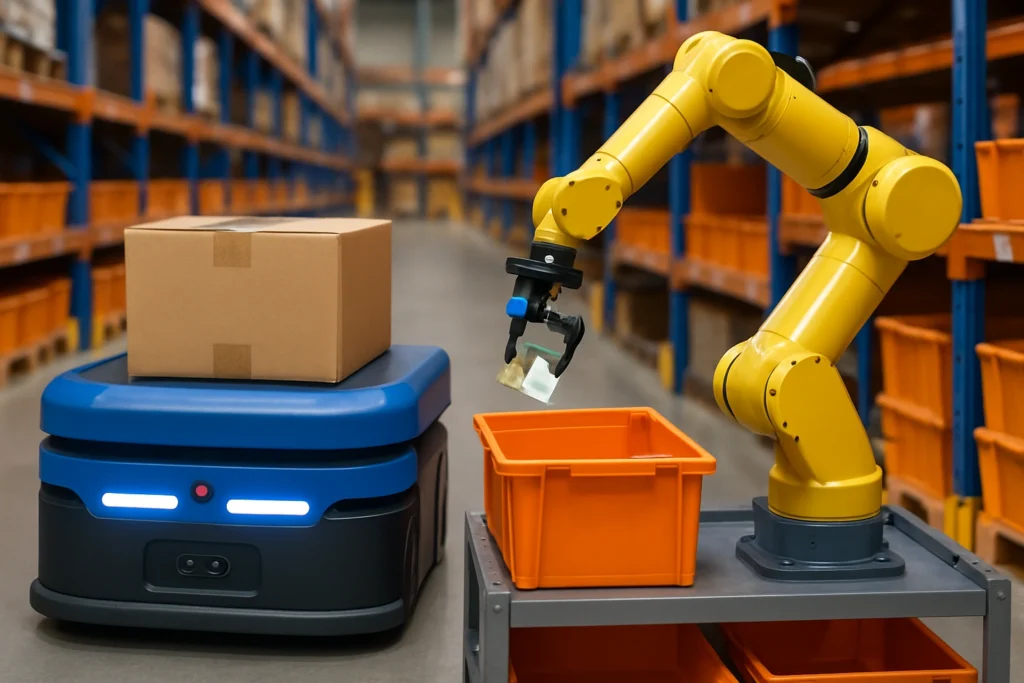

Robotics bring consistency and endurance to warehousing tasks. Unlike humans, robots don’t tire or lose focus. In accuracy-driven operations, this matters.
Key Robotics Applications include:
Robotic Picking Systems: Automated arms with advanced grippers reduce picking errors, ensuring the right item is selected every time.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These mobile robots transport items seamlessly, minimizing misplacement.
Inventory Robotics: Robots equipped with cameras and sensors scan inventory in real time, keeping stock counts accurate.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Working alongside humans, cobots enhance efficiency while reducing error-prone tasks.
By improving robotic picking accuracy and reducing reliance on human judgment, robotics lay the groundwork for higher precision in warehouses.
AI: The Brain Behind the Precision
AI serves as the cognitive engine for smart robotics systems, providing the crucial layers of intelligence necessary for accurate handling.
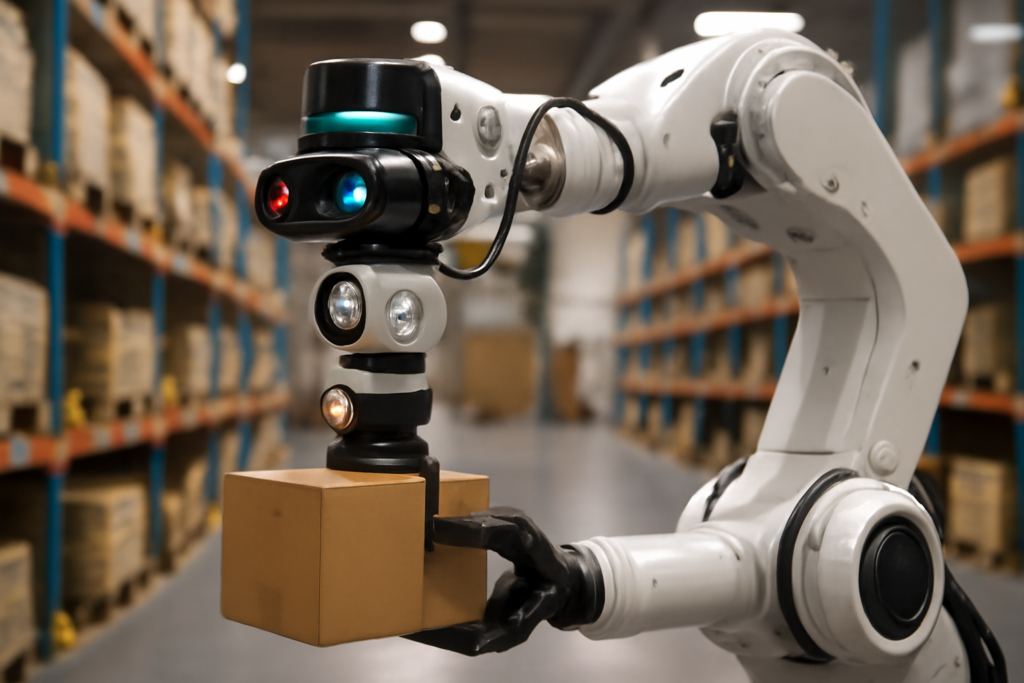
1. Computer Vision and Object Recognition
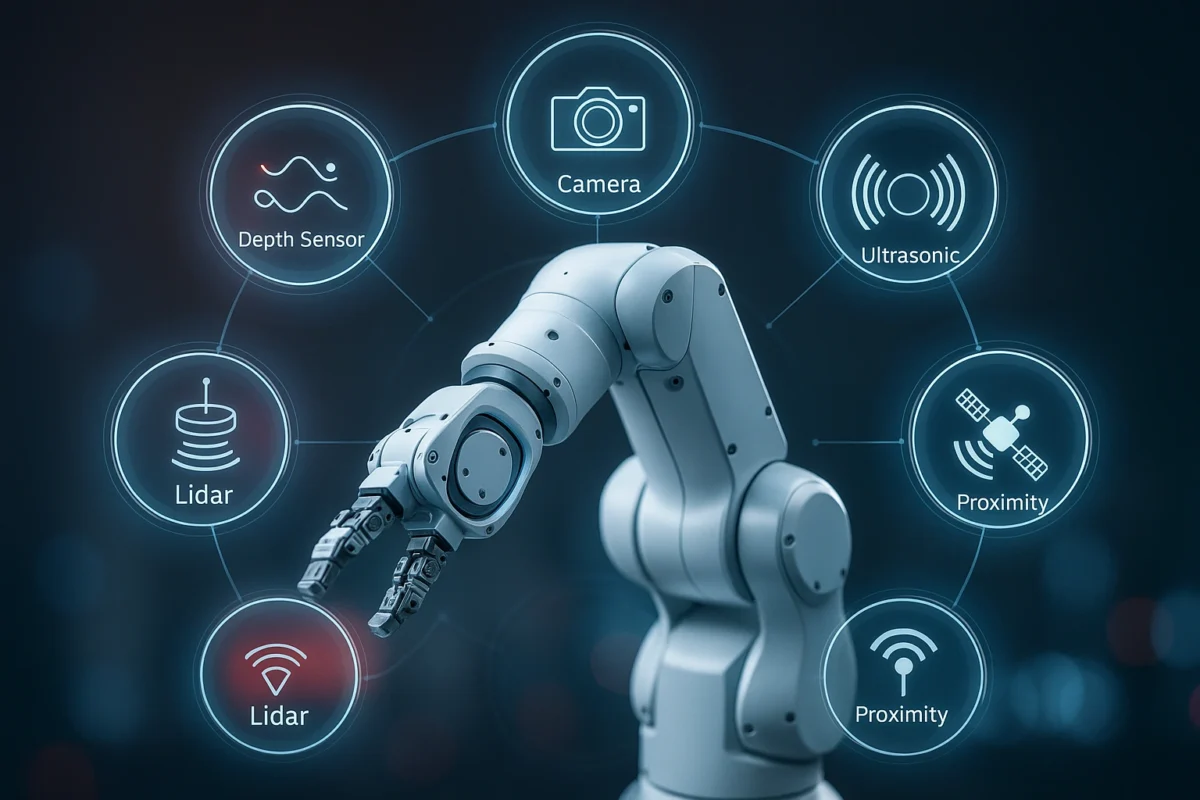
The primary function of AI in this context is to see the world as data. Using high-resolution cameras, 3D scanners, and advanced computer vision algorithms, the robot can:
- Differentiate Between SKUs: AI can instantly distinguish between two visually similar products (e.g., two different flavors of the same brand of cereal box) by analyzing minute details, such as subtle packaging changes or small text differences that a human might overlook in haste.
- Determine Pose and Orientation: Crucially, the AI calculates the exact position and orientation (pose) of the target item within the bin or on the shelf. This provides the robot arm with the necessary coordinates for a precise grip.
- Handle Clutter: Unlike simpler systems, AI robotics warehouse solutions use deep learning to understand cluttered bins, effectively separating the target item from surrounding noise and shadows.
2. Predictive Grasping and Force Control
Once the AI has identified the target, it uses machine learning to plan the perfect grasp which is a measure of robot precision:
- Grip Optimization: The model selects the ideal end-effector (gripper) and determines the exact pressure and angle required to secure the item without damaging it. For a fragile item, it might use a gentle vacuum cup; for a heavy box, a more robust parallel gripper.
- Weight and Material Prediction: By analyzing the visual data and comparing it to its inventory database, the AI can predict the item’s weight and material properties, adjusting the picking force in real-time. This dynamic force control minimizes product damage, a common source of error and cost in manual picking.
How AI and Robotics Work Together
The true breakthrough happens when AI and robotics combine. Robotics provides the hands, while AI supplies the brain.
Examples of AI-Robotics Synergy:
Smart Picking: A robot arm identifies items via AI-powered vision, validates them against the order, and executes precise picks.
Automated Inventory Management: AI algorithms sync with robotic scanners to update stock levels instantly.
Error Prevention: If a robot misidentifies an item, AI cross-checks data from sensors and corrects the action.
Dynamic Pathfinding: AI guides warehouse robots through optimized routes, avoiding congestion and ensuring fast delivery.
Together, these systems achieve robot precision at a level impossible with traditional automation alone.
Benefits of AI-Driven Warehouse Accuracy Robotics
Adopting smart robotics systems in warehouses unlocks multiple benefits:
Higher Inventory Accuracy
Robots paired with AI achieve near-perfect stock counts, minimizing shrinkage and discrepancies.
Fewer Picking Errors
Intelligent robots validate every pick against digital orders, reducing costly mistakes.
Faster Fulfillment
By combining robotic speed with AI optimization, warehouses fulfill orders faster without sacrificing quality.
Cost Savings
Reduced returns, lower labor costs, and optimized operations lead to significant long-term savings.
Scalability
As order volumes grow, AI-driven robots can adapt seamlessly without requiring massive workforce changes.
Improved Safety
With AI monitoring, robots avoid collisions and handle repetitive or dangerous tasks, creating safer workplaces.
Challenges in AI and Robotics Adoption
Despite clear benefits, challenges remain:
High Implementation Costs: Robotics systems and AI integration require significant investment.
Data Overload: Massive streams of inventory and sensor data must be processed effectively.
Integration Complexity: Aligning AI with existing warehouse management robotics can be challenging.
Skill Gaps: Workforce training is essential to manage and maintain advanced systems.
Addressing these challenges requires strong planning, reliable robotic logistics software, and phased adoption strategies.
The Future of AI and Warehouse Accuracy Robotics

Looking ahead, AI and robotics will continue to evolve:
Swarm Robotics: Coordinated fleets of robots will handle complex tasks collectively.
Self-Healing AI Systems: Predictive maintenance will reduce downtime and improve warehouse uptime robots.
Digital Twins: Real-time simulations will test warehouse layouts for maximum efficiency.
Human-Robot Collaboration: AI will create safer, more intuitive environments for people and machines to work together.
Warehouses that invest now in warehouse automation solutions will set the benchmark for precision and reliability.
Conclusion
The blend of AI and robotics is revolutionizing how accurate our warehouses can be. Robots handle the work with speed and consistency, while AI provides the intelligence and flexibility. When combined, these smart robotic systems drastically cut down on errors, lead to better inventory optimization, and significantly boost productivity across the board.
As warehouse automation keeps advancing, companies that adopt this powerful combination won’t just see greater accuracy; they’ll also build a stronger, more resilient business better equipped to handle today’s tough logistics competition.
FAQ: Warehouse Accuracy Robotics
How do AI and robotics improve warehouse accuracy compared to manual methods?
Robots reduce human error, while AI ensures tasks are optimized and verified, creating near-perfect accuracy.
Are AI-driven robotics systems suitable for small warehouses?
Yes. Scalable solutions exist, though initial costs can be a barrier. Cloud-based AI tools make adoption easier for smaller facilities.
What industries benefit most from AI-robotics warehouses?
E-commerce, retail, pharmaceuticals, and food logistics gain the most due to high SKU counts and strict accuracy needs.
Can AI prevent warehouse downtime?
Yes. AI predicts equipment failures and schedules proactive maintenance, keeping robots and systems operational.